Getting Started
Ameba ARDUINO: Getting Started with AMB23
Required Environment
AMB23 board currently supports Windows OS 32-bits and 64-bits (WIN7/8/10), Linux OS (Ubuntu 18 LTS/20 LTS/latest) and macOS operating systems. Please use the latest OS version to have the best experiences. In this documentation, please use the latest version Arduino IDE (at least version 1.8.12).
Introduction to AmebaD[AMB23]
Ameba is an easy-to-program platform for developing all kind of IoT applications. AmebaD is equipped with various peripheral interfaces, including WiFi, GPIO INT, I2C, UART, SPI, PWM, ADC. Through these interfaces, AmebaD can connect with electronic components such as LED, switches, manometer, hygrometer, PM2.5 dust sensors, …etc.
The collected data can be uploaded via WiFi and be utilized by applications on smart devices to realize IoT implementation.
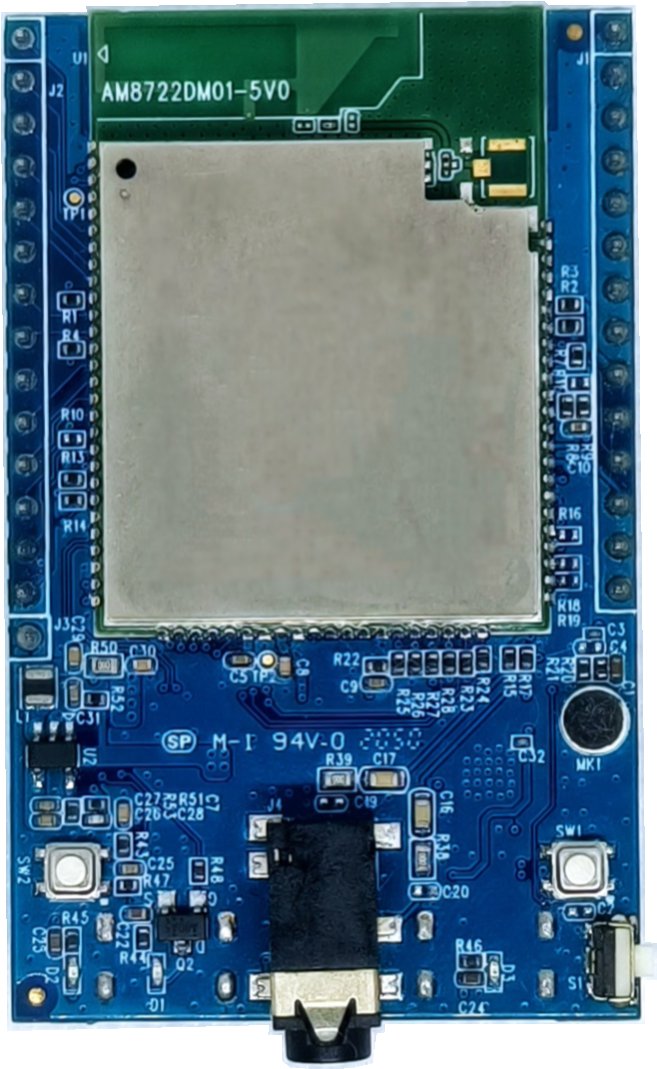
AMB23 has smaller size than Arduino Uno, as shown in the above figure.
AMB23 uses Micro USB to supply power, which is common in many smart devices.
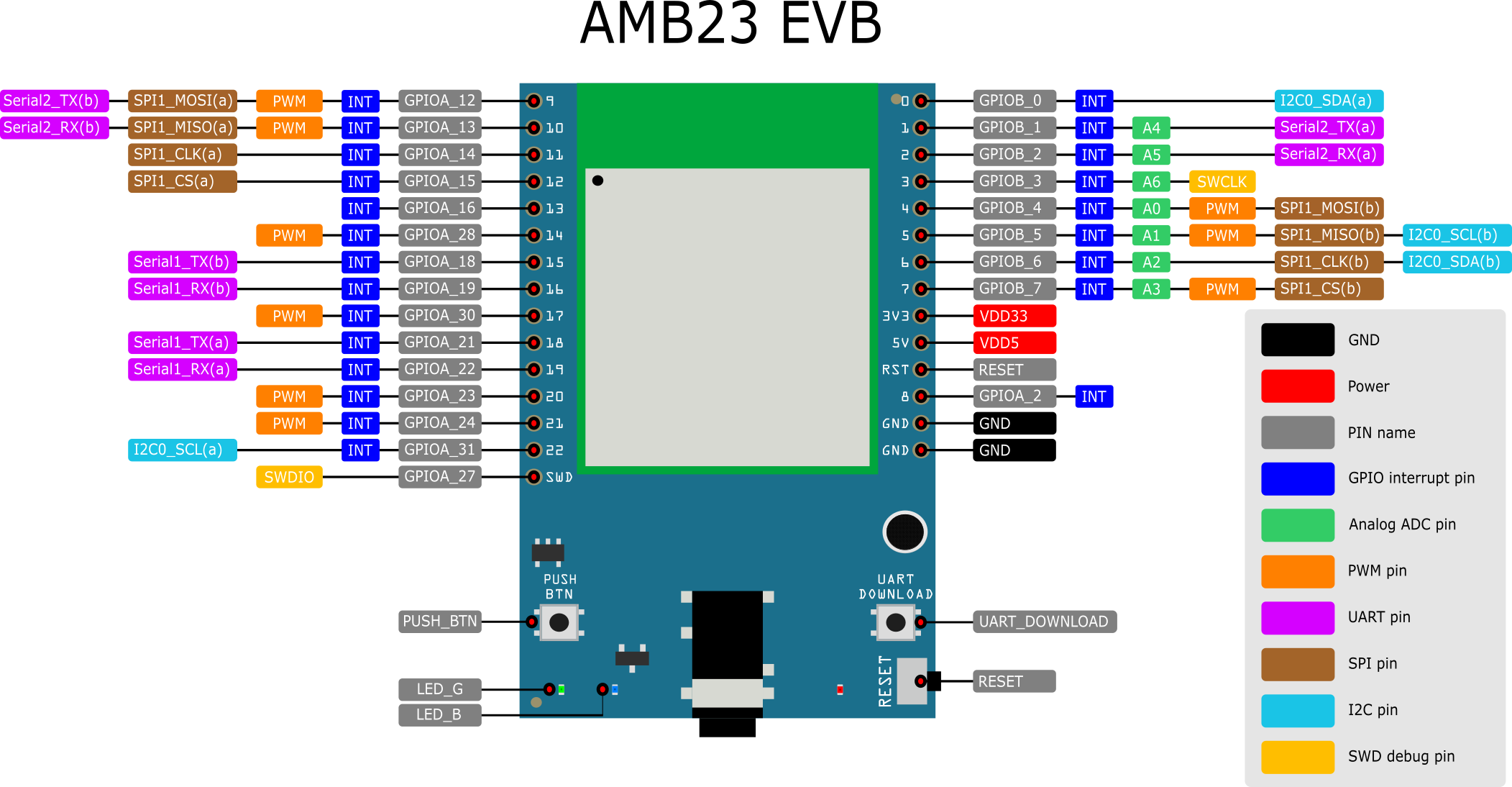
Please refer to the following figure and table for the pin diagram and function of AMB23.
# |
PIN name |
GPIO INT |
ADC |
PWM |
UART |
SPI |
I2C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
D0 |
GPIOB_0 |
✓ |
I2C0 SDA |
||||
D1 |
GPIOB_1 |
✓ |
A4 |
Serial2_TX |
|||
D2 |
GPIOB_2 |
✓ |
A5 |
Serial2_RX |
|||
D3 |
GPIOB_3 |
✓ |
A6 |
||||
D4 |
GPIOB_4 |
✓ |
A0 |
✓ |
|||
D5 |
GPIOB_5 |
✓ |
A1 |
✓ |
I2C0 SCL |
||
D6 |
GPIOB_6 |
✓ |
A2 |
I2C0 SDA |
|||
D7 |
GPIOB_7 |
✓ |
A3 |
✓ |
|||
D8 |
GPIOA_2 |
✓ |
|||||
D9 |
GPIOA_12 |
✓ |
✓ |
Serial2_TX |
SPI1_MOSI |
||
D10 |
GPIOA_13 |
✓ |
✓ |
Serial2_RX |
SPI1_MISO |
||
D11 |
GPIOA_14 |
✓ |
SPI1_CLK |
||||
D12 |
GPIOA_15 |
✓ |
SPI1_CS |
||||
D13 |
GPIOA_16 |
✓ |
|||||
D14 |
GPIOA_28 |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
D15 |
GPIOA_18 |
✓ |
Serial1_TX |
||||
D16 |
GPIOA_19 |
✓ |
Serial1_RX |
||||
D17 |
GPIOA_30 |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
D18 |
GPIOA_21 |
✓ |
Serial1_TX |
||||
D19 |
GPIOA_22 |
✓ |
Serial1_RX |
||||
D20 |
GPIOA_23 |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
D21 |
GPIOA_24 |
✓ |
✓ |
||||
D22 |
GPIOA_31 |
✓ |
I2C0 SCL |
Setting up Development Environment
Step 1. Installing the Driver
First, connect AMB23 to the computer via Micro USB (same as power):
If this is the first time you connect AMB23 to your computer, the USB driver for AMB23 will be automatically installed.
If you have driver issue of connect board to your computer please go to here for USB driver.
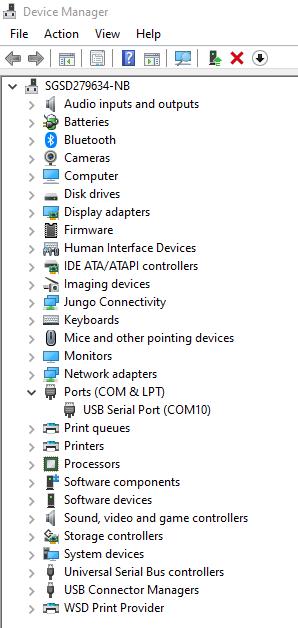
You can check the COM port number in Device Manager of your computer:
Step 2. Set up Arduino IDE
From version 1.6.5, Arduino IDE supports third-party hardware. Therefore, we can use Arduino IDE to develop applications on AMB23, and the examples of Arduino can run on AMB23 too. Refer to basic example link.
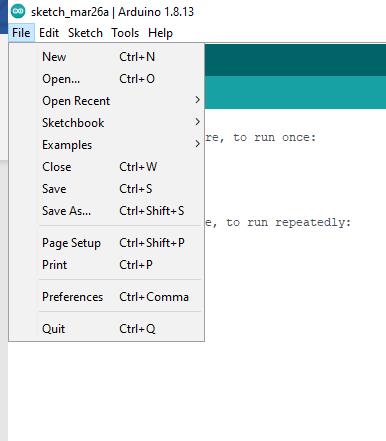
Arduino IDE can be downloaded in the Arduino website: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software When the installation is finished, open Arduino IDE. To set up AMB23 correctly in Arduino IDE, go to “File” -> “Preferences”.
And paste the following URL into “Additional Boards Manager URLs” field:
https://github.com/ambiot/ambd_arduino/raw/master/Arduino_package/package_realtek.com_amebad_index.json
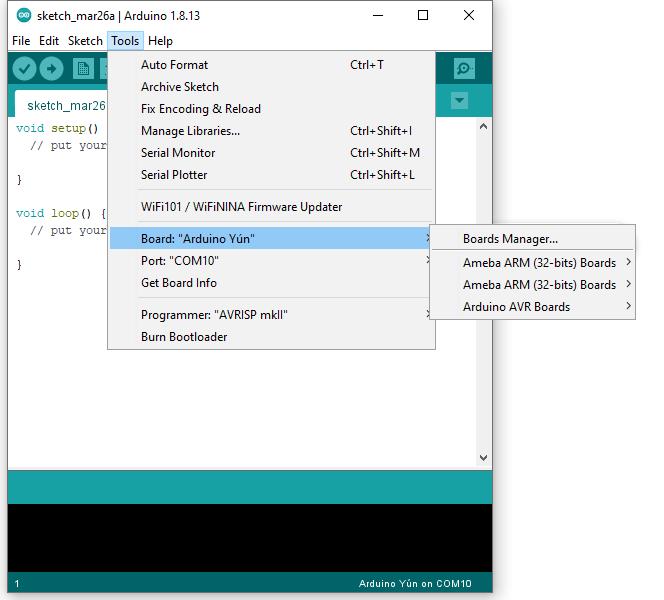
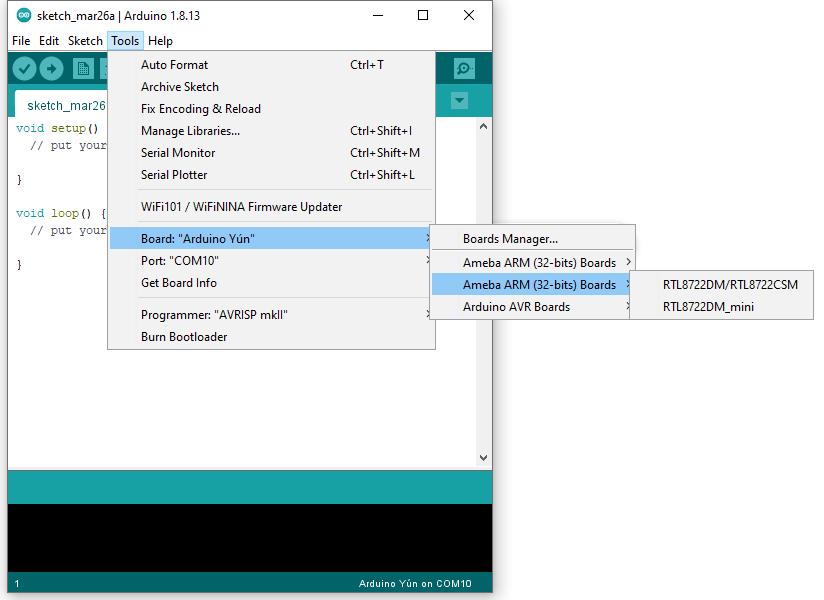
Next, go to “Tools” -> “Board” -> “Boards Manager”:
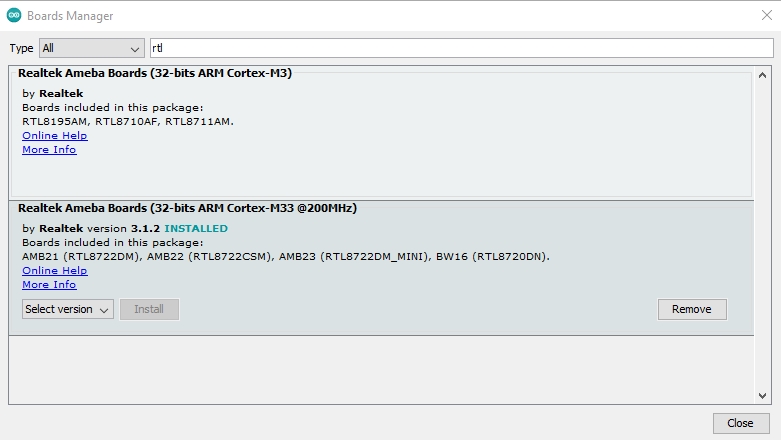
The “Boards Manager” requires about 10~20 seconds to refresh all hardware files (if the network is in bad condition, it may take longer). Every time the new hardware is connected, we need to reopen the Board Manager. So, we close the “Boards Manager”, and then open it again. Find “Realtek Ameba Boards (32-bits ARM Cortex-M33 @200MHz)” in the list, click “Install”, then the Arduino IDE starts to download required files for AmebaD.
If you are facing GitHub downloading issue, please refer to the following link at Download/Software Development Kit. There are 3 sections:
“AmebaD_Arduino_patch1_SDK”, please select at least 1 of the SDKs. There are 5 latest released SDK options.
“AmebaD_Arduino_patch2_Tools”, please select according to your operation system. There are Windows, Linux and MacOS.
“AmebaD_Arduino_Source_Code”, this section is optional download only wants to refer the latest source code.
Download the files selected, then unzip (patch1 and patch2 are compulsory). There are “Install.doc”/“Install.pdf” for you to refer installation steps. According to your system, please run the installation tool in the “Offline_SDK_installation_tool” folder.
After the installation tool running successfully, you may open Arduino IDE and proceed to “Tools” -> “Board“ -> “Boards Manager…”. Try to find “Realtek Ameba Boards (32-bits ARM Cortex-M33 @200MHz)”` in the list, click “Install”, then the Arduino IDE starts to download required files for AmebaD.
Finally, we select AmebaD as current connected board in “Tools” -> “Board” -> “Ameba ARM (32-bits) Boards” ->” RTL8722DM MINI”:
Try the First Example
Step 1. Compile & Upload
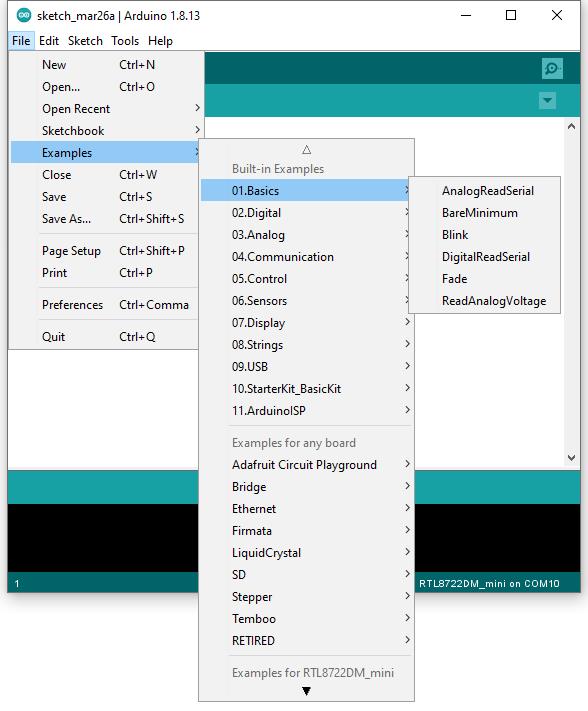
Arduino IDE provides many built-in examples, which can be compiled, uploaded and run directly on the boards. Here, we take the “Blink” example as the first try.
Open “File” -> “Examples” -> “01.Basics” -> “Blink”:
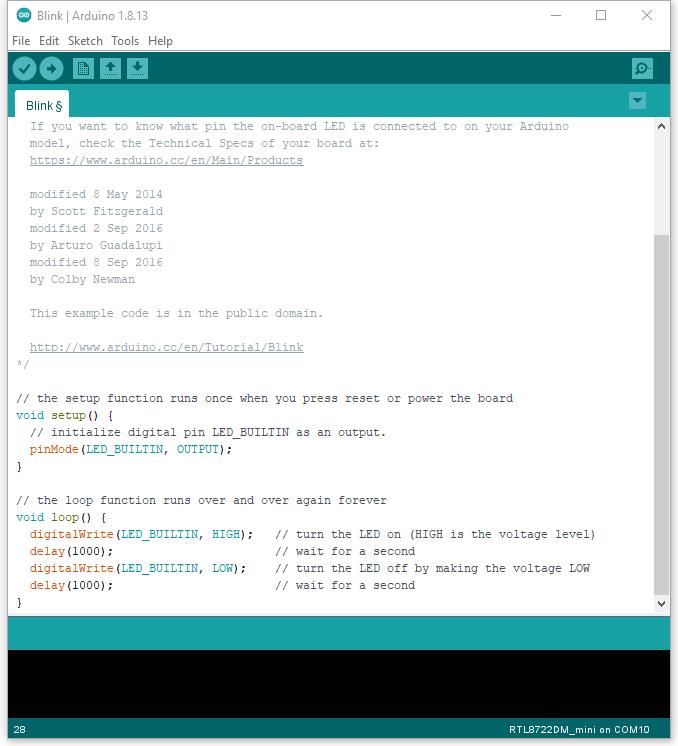
Arduino IDE opens a new window with the complete sample code.
Tip
There are two onboard LEDs on AMB23, LED_B and LED_G (Blue and Green),
the default LED_BUILTIN is the onboard blue LED.
Change LED_BUILTIN to LED_B or LED_G for different colour.
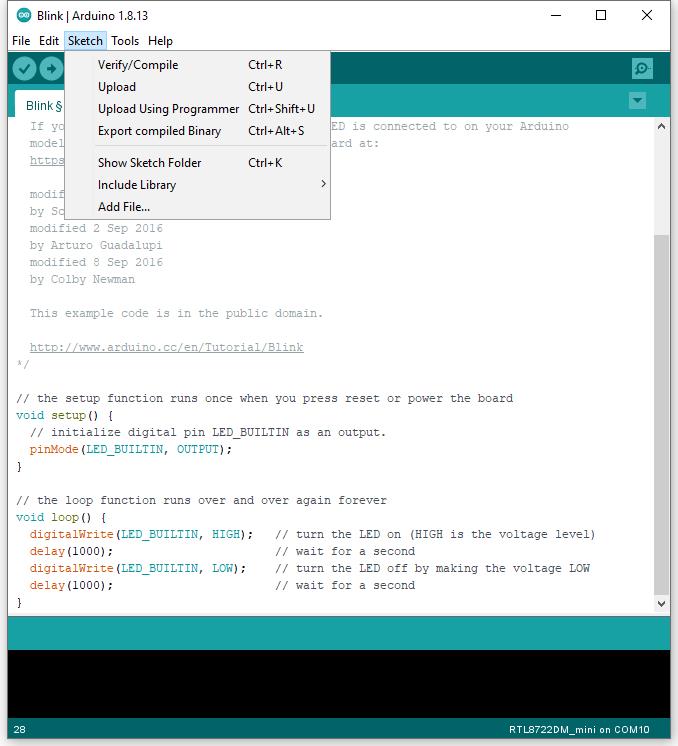
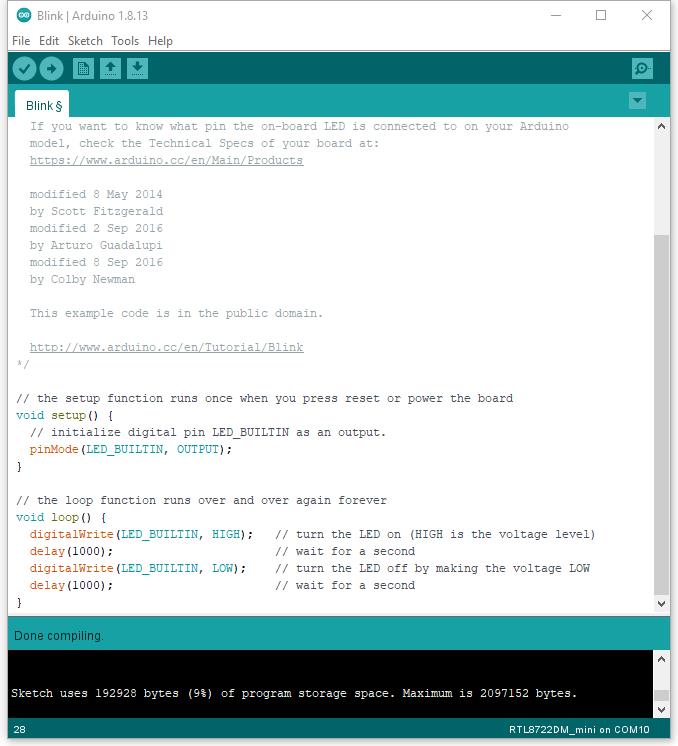
Next, we compile the sample code directly; click “Sketch” -> “Verify/Compile”
Arduino IDE prints the compiling messages in the bottom area of the IDE window. When the compilation is finished, you will get the message similar to the following figure:
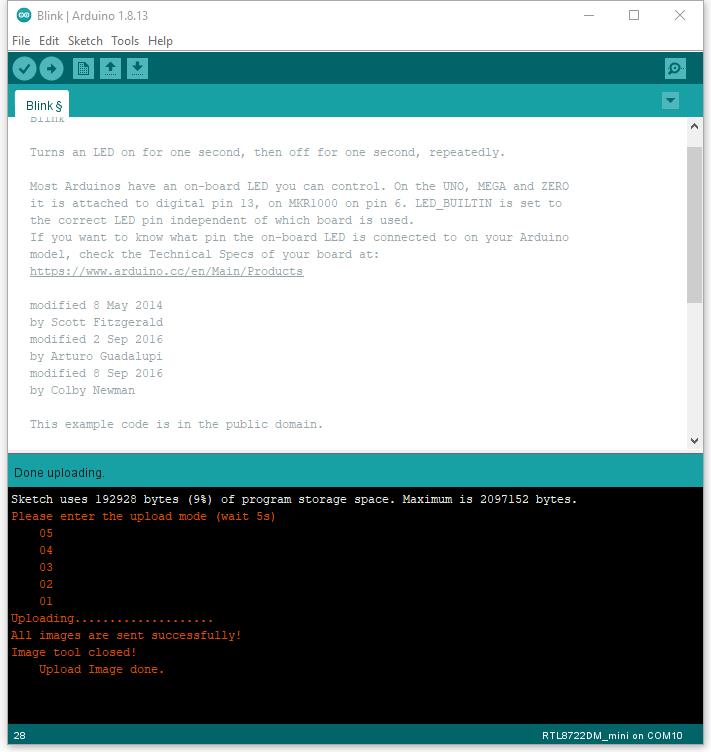
Afterwards, we will upload the compiled code to AMB23. Please make sure AMB23 is connected to your computer, then click “Sketch” -> “Upload”.
The Arduino IDE will compile first then upload. Users are required to enter the upload mode of the board.
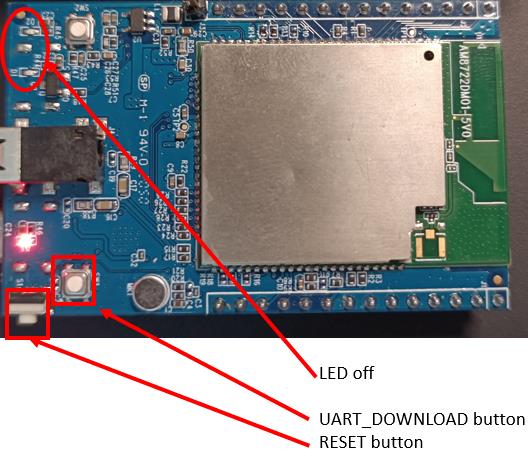
To enter the upload mode, first press and hold the UART_DOWNLOAD button, then press and release the RESET button, lastly release the UART_DOWNLOAD button. There is a 5-seconds count down set as a reminder to enter the upload mode.
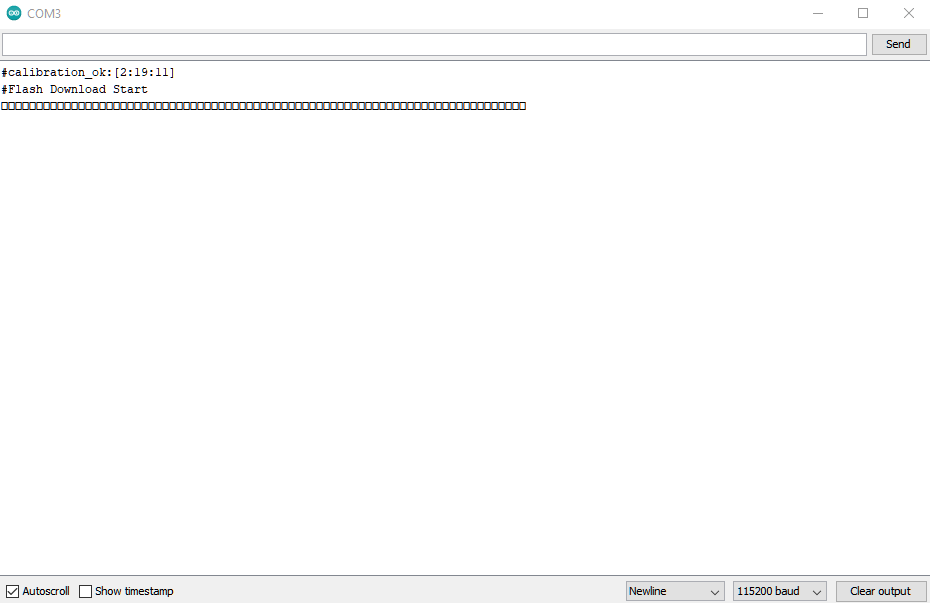
It is optional for users to check if the board entered the upload mode. Open serial monitor/terminal and look for “#Flash Download Start”.
Note
It is normal that some serial terminals may show unknown characters as the following picture.
Again, during the uploading procedure the IDE prints messages. Uploading procedure takes considerably longer time (about 30 seconds to 1 minute). When upload completed, the “Done uploading” message is printed.
Step 2.Run the Blink example
In each example, Arduino not only provides sample code, but also detailed documentation, including wiring diagram, sample code explanation, technical details, …etc. These examples can be directly used on AMB23. So, we can find the detailed information of the “Blink” example: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/BuiltInExamples/Blink
In short, for AMB23, the example can be run on both onboard LEDs (green or blue) or external LED (use any GPIO pins for signal output).
Finally, press the RESET button, and you can see the LED blinking.
(End)
Note
If you face any issue, please refer to the FAQ and Trouble shooting sections on Support page.