Getting Started
Setup of the GCC Development Environment
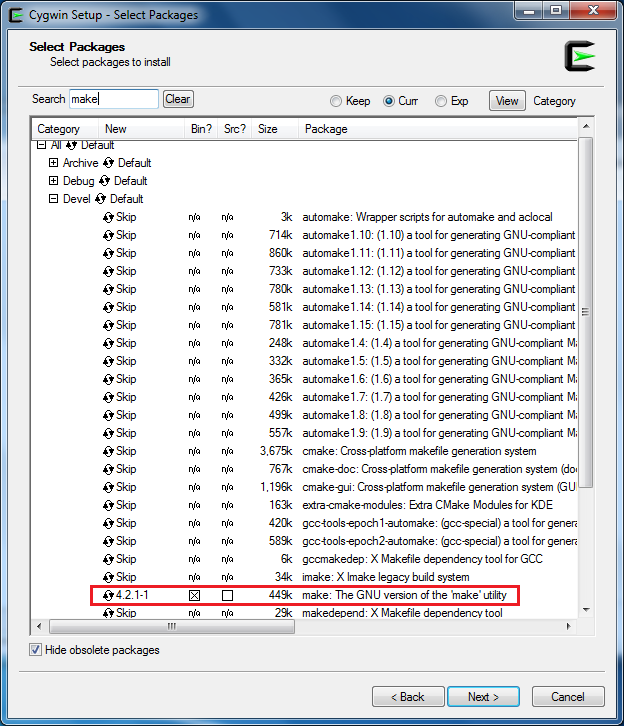
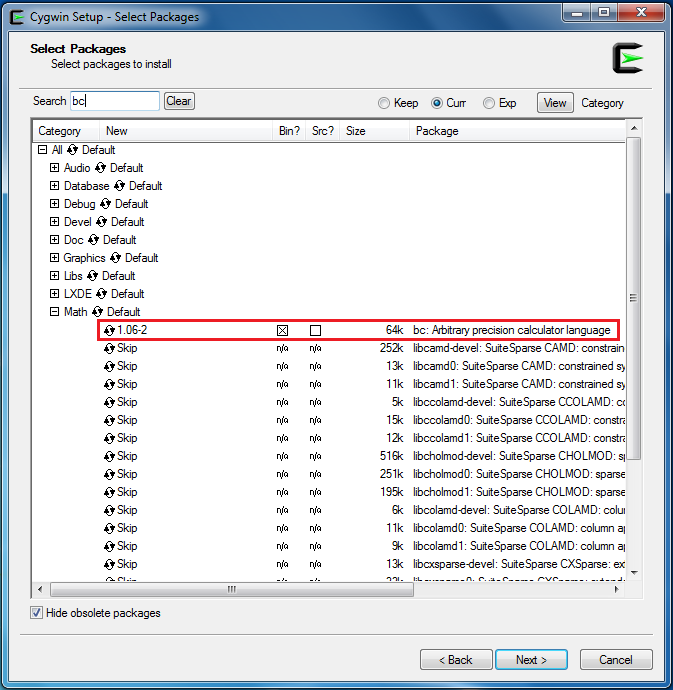
Cygwin as the GCC development environment. Cygwin is a large collection of GNU and open source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows.Cygwin is supported both for 32-bit Windows and 64-bit Windows.Cygwin package, include ‘Devel -> make’ and ‘Math -> bc’ utilities on the Select Packages page, as below shows.Note
For Linux, refer to AN0400 Ameba-D Application Note v12.pdf to build the GCC development environment.
Knowledge about Ameba-D Demo Board
The hardware block diagram of Ameba-D demo board is shown below.
Connection to Log Console
SecureCRT/teraterm/putty and etc. We will take our internal tool as an example.Building the First GCC Project on Ameba-D
The following steps are for first-time developer to build GCC project, under existing RTK SDK.
Cygwin terminal and use $ cd command to change directory to KM0 or KM4 project directory of Ameba-D SDK.Note
You need to replace the {path} to your own SDK location, and add “cygdrive” prefix in front of the SDK location, so that Cygwin can access your file system.
$ cd /cygdrive/{path}/project/realtek_amebaD_va0_example/GCC-RELEASE/project_lp$ cd /cygdrive/{path}/project/realtek_amebaD_va0_example/GCC-RELEASE/project_hp
Linux, open its own terminal and use $ cd command to change directory to KM0 or KM4 project directory of Ameba-D SDK.
$ cd /{path}/project/realtek_amebaD_va0_example/GCC-RELEASE/project_lp$ cd /{path}/project/realtek_amebaD_va0_example/GCC-RELEASE/project_hp
To build SDK for normal image, simply use $ make all command under the corresponding project directories on Cygwin (Windows) or terminal (Linux).
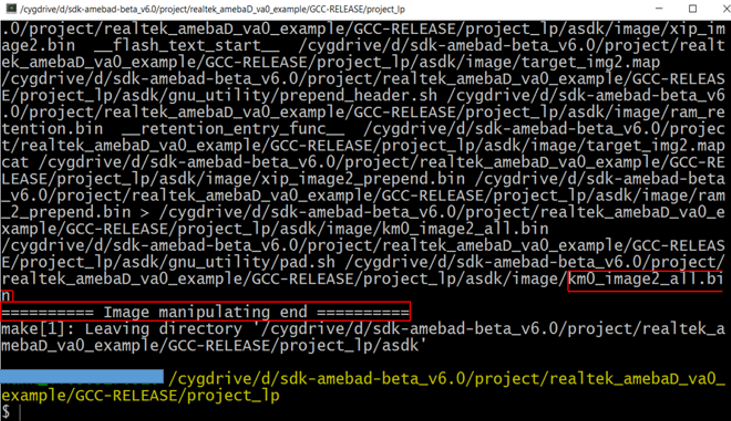
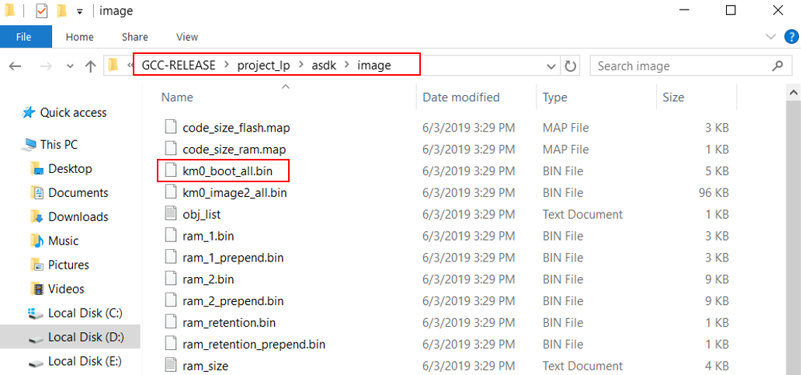
KM0 project For KM0 project, if the terminal contains “km0_image2_all.bin” and “Image manipulating end” output message, it means that the image has been built successfully, as below shows.
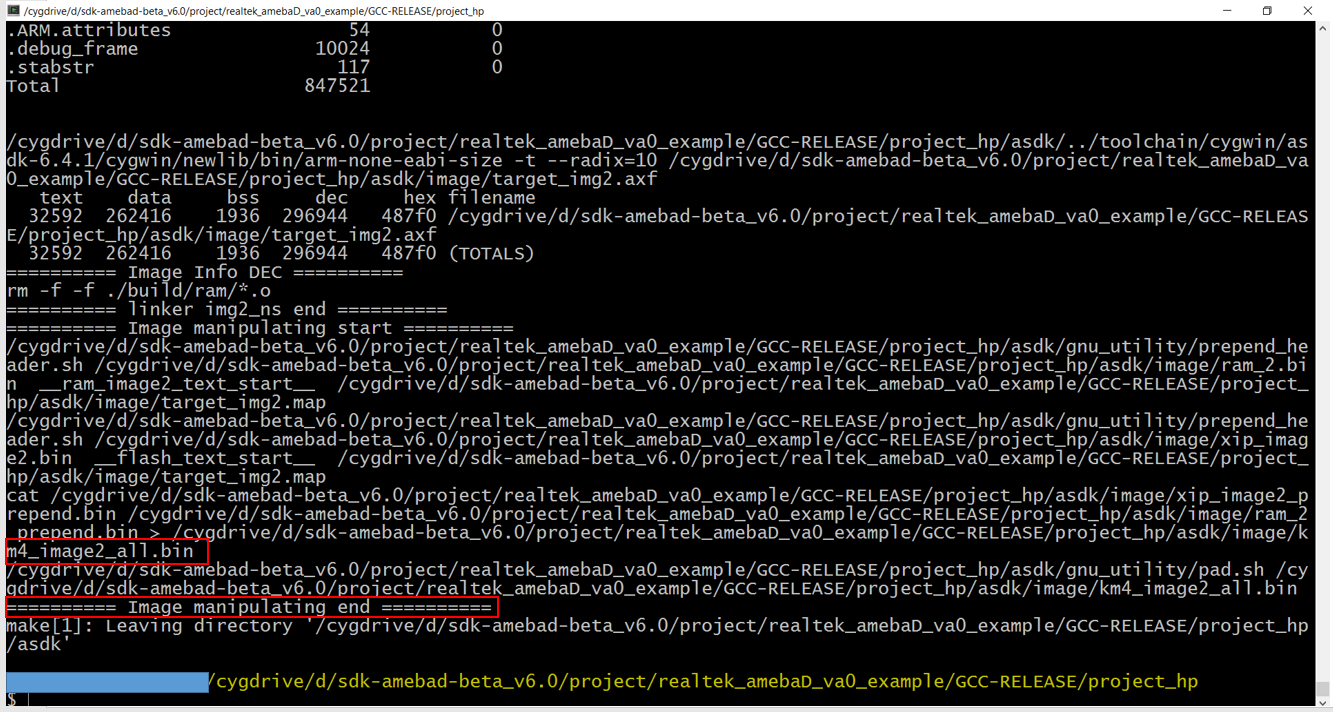
$ make clean to clean and then redo the make procedure.project/realtek_amebaD_va0_example/GCC-RELEASE/project_lp/asdk/image , as below shows.KM4 project For KM4 project, if the terminal contains “km0_image2_all.bin” and “Image manipulating end” output message, it means that the image has been built successfully, as below shows.
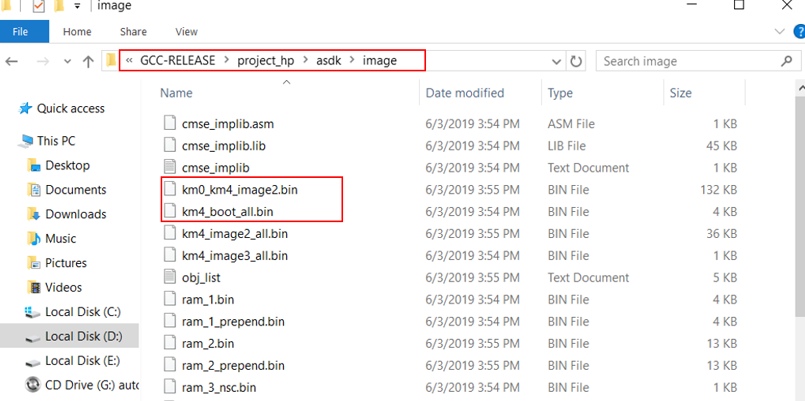
$ make clean to clean and then redo the make procedure.project/realtek_amebaD_va0_example/GCC-RELEASE/project_hp/asdk/image, as below shows.Downloading Images to Ameba-D
Realtek provides an image tool to download images on windows.
Assuming that the ImageTool on PC is a server, it sends images files to Ameba (client) through UART. To download image from server to client, the client must enter uart download first.
Enter into UART_DOWNLOAD mode.
Push the UART DOWNLOAD button and keep it pressed.
Re-power on the board or press the Reset button.
Release the UART DOWNLOAD button.
Now, Ameba board gets into UART_DOWNLOAD mode and is ready to receive data.
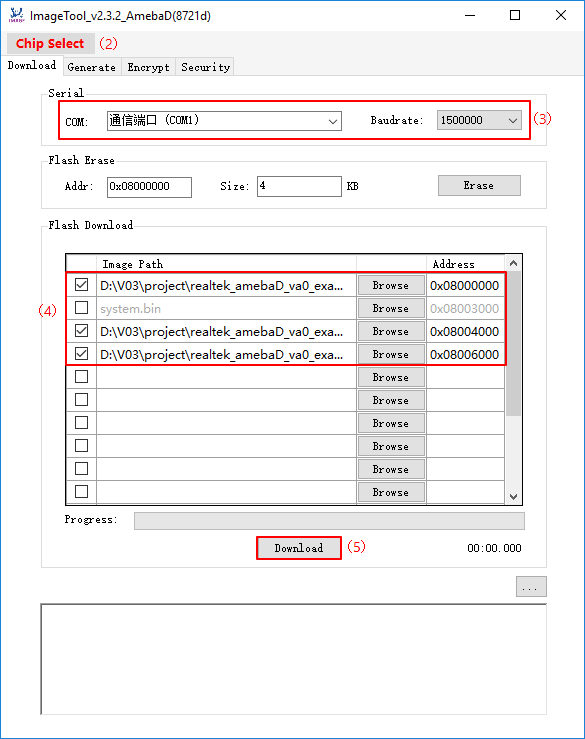
Click Chip Select(in red) on UI and select chip (AmebaD or AmebaZ).
Select the corresponding serial port and transmission baud rate. The default baudrate is 1.5Mbps (recommended).
Click the Browse button to select the images (km0_boot_all.bin/km4_boot_all.bin/km0_km4_image2.bin) to be programmed and input addresses.
- The image path is located in:
{path}\project\realtek_amebaD_va0_example\GCC-RELEASE\project_lp\asdk\imageand{path}\project\realtek_amebaD_va0_example\GCC-RELEASE\project_hp\asdk\image,where {path} is the location of the project on your own computer. The default target address is the SDK default image address, you can use it directly.
Click Download button to start. The progress bar will show the transmit progress of each image. You can also get the message of operation successfully or errors from the log window.