HTTP - Set up Server to Control LED
Materials
AmebaD [AMB21 / AMB22 / AMB23 / BW16] x 1
Breadboard x 1
LED x 1
1KΩ Resistor x 1
Procedure
In this example, we connect Ameba to WiFi and use Ameba as server, the user can control the LED on/off through a webpage.
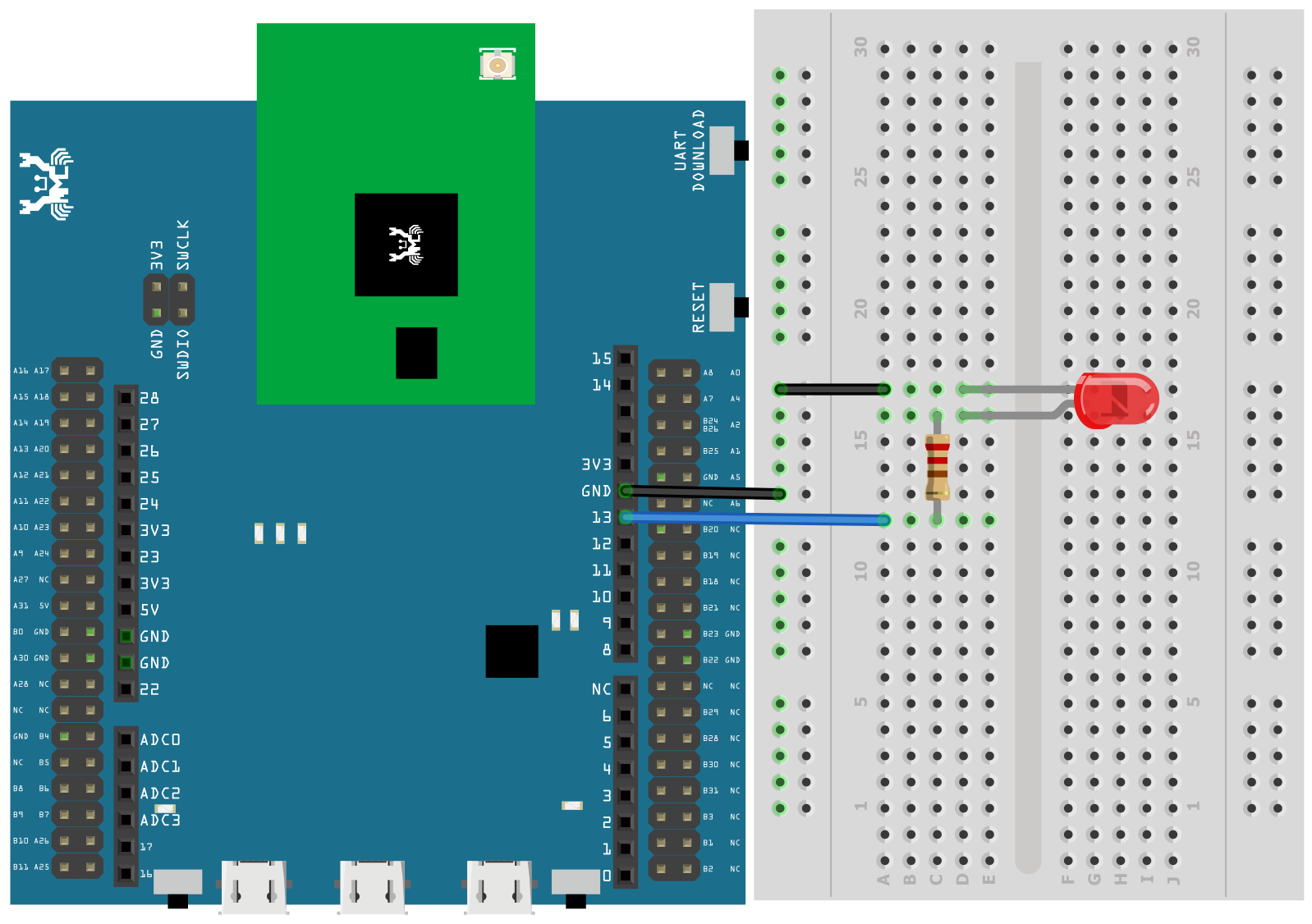
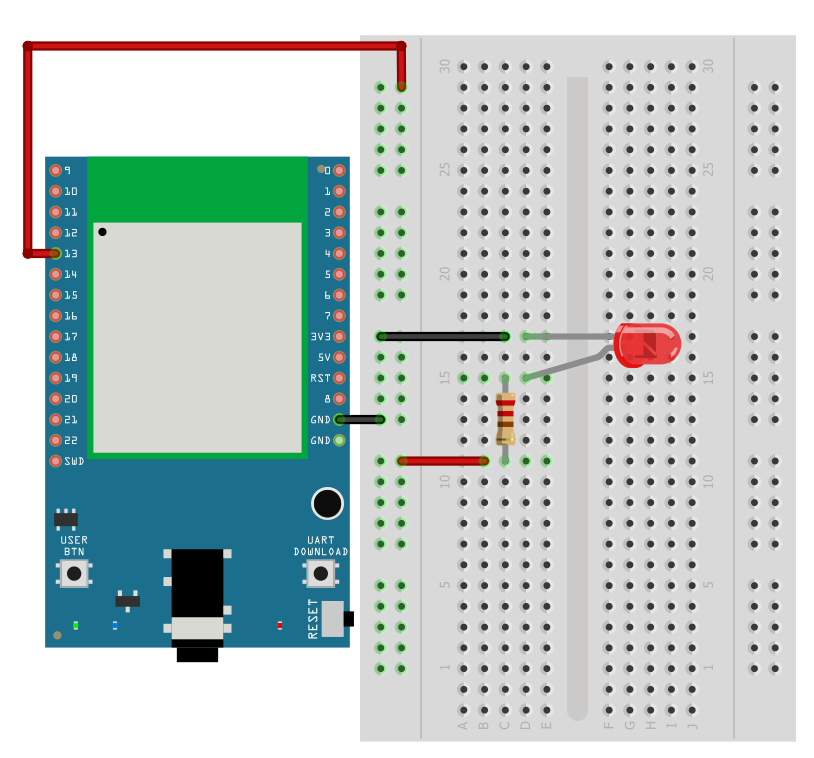
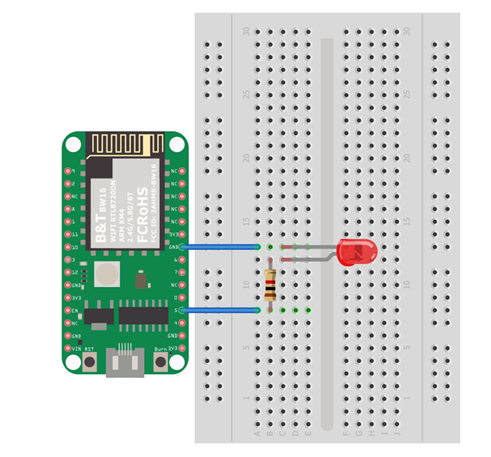
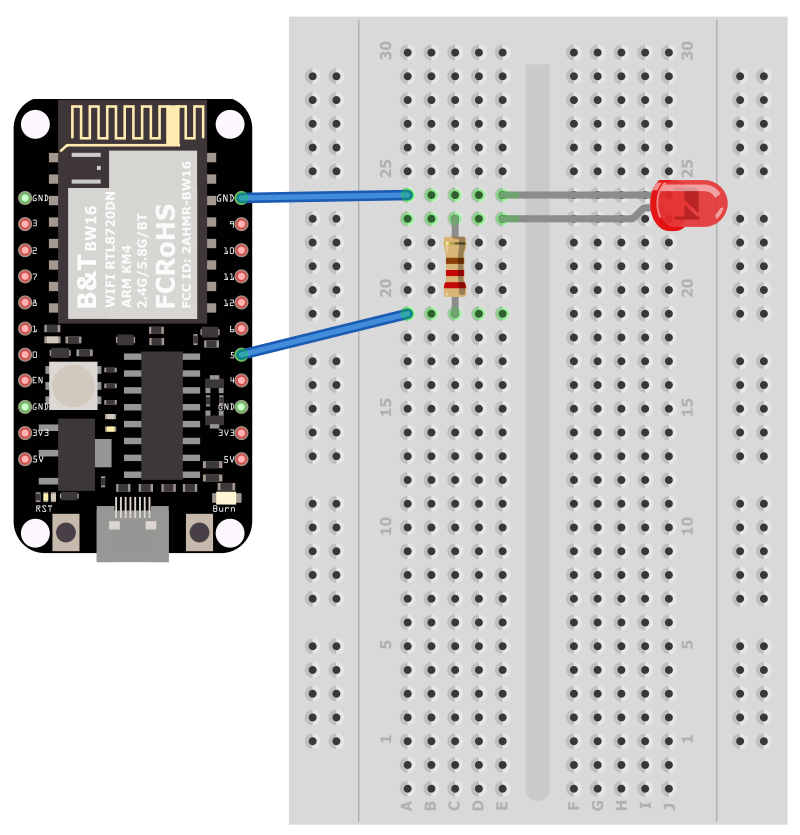
First, connect Ameba with the LED. In a LED, the longer pin is the positive pole, and the shorter pin is the negative pole. So, we connect the shorter pin to GND and connect the longer pin to D13. Additionally, to avoid the electric current exceeds the tolerance of the LED and causes damage, we connect a resistance on the positive pole.
AMB21 / AMB22 Wiring Diagram:
AMB23 Wiring Diagram:
BW16 Wiring Diagram:
Note
For BW16 board, you may consider to re-define “LED_PIN” macro to 10 for built-in green LED, or 11 for blue built-in LED, or 12 for red built-in LED to avoid using extra components.
BW16-TypeC Wiring Diagram:
“File” → “Examples” → “WiFi” → “SimpleWebServerWiFi”
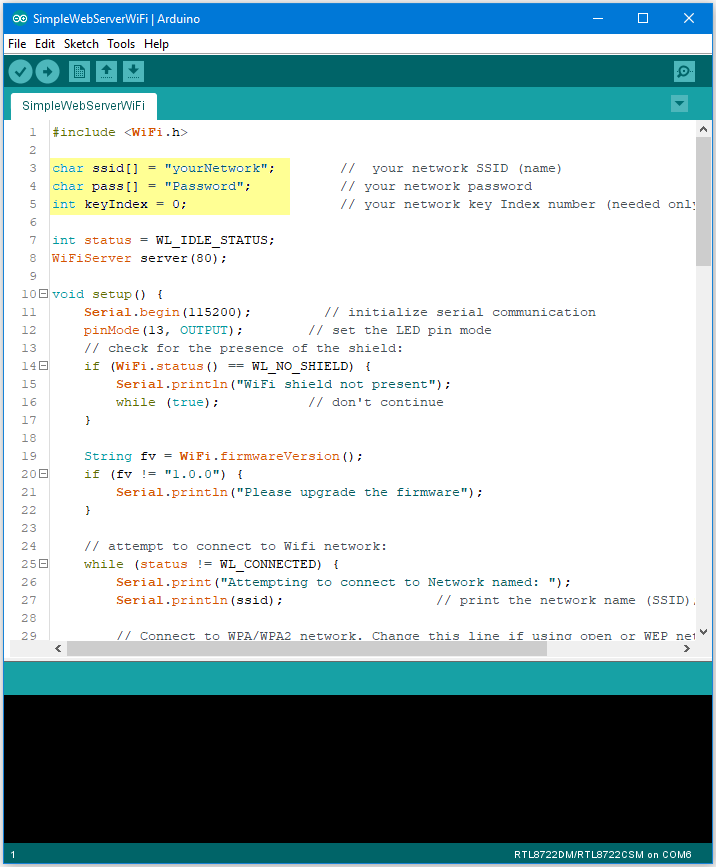
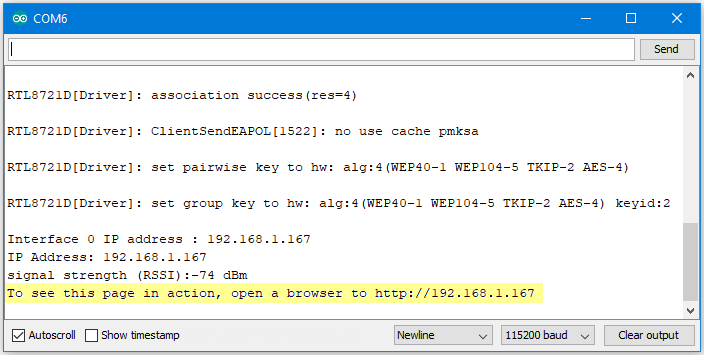
Upload the code and press the reset button on Ameba. When the connection is established, you will see the message:
“To see this page in action, open a browser to http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx”
in the Arduino IDE as shown in the figure:
Next, open the browser of a computer or a cell phone under the same WiFi domain, enter the address in the message.
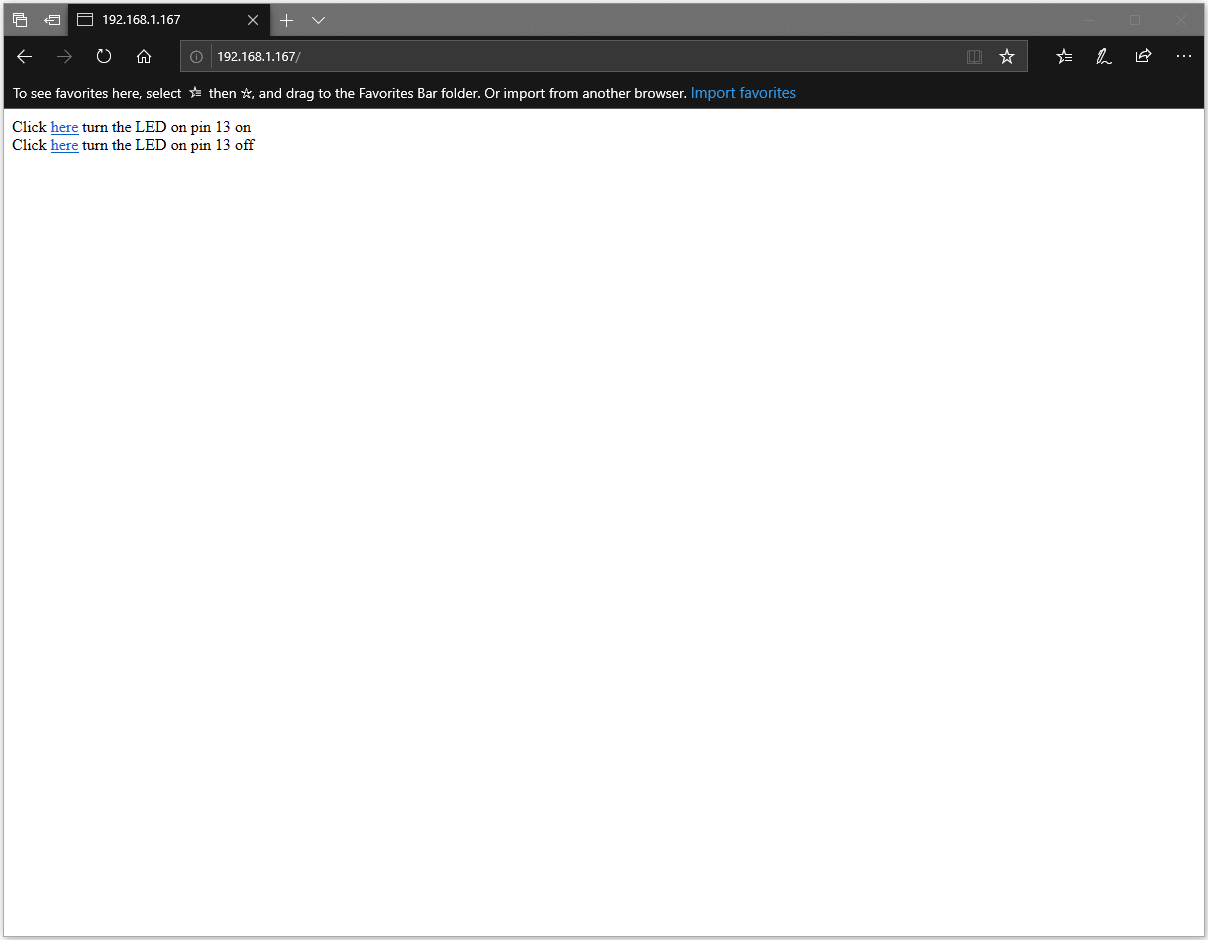
In the webpage, you can turn on/off the LED.
Code Reference
Use WiFi.begin() to establish WiFi connection.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiBegin
To get the information of a WiFi connection:
Use WiFi.SSID() to get SSID of the current connected network.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiSSID
Use WiFi.RSSI() to get the signal strength of the connection. https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiRSSI
Use WiFi.localIP() to get the IP address of Ameba.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiLocalIP
Use WiFiServer server() to create a server that listens on the
specified port.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiServer
Use server.begin() to tell the server to begin listening for incoming
connections.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiServerBegin
Use server.available() to get a client that is connected to the server
and has data available for reading.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiServerAvailable
Use client.connected() to get whether or not the client is connected.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiClientConnected
Use client.println() to print data followed by a carriage return and
newline.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiClientPrintln
Use client.print() to print data to the server that a client is
connected to.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiClientPrint
Use client.available() to return the number of bytes available for
reading.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiClientAvailable
Use client.read() to read the next byte received from the server the
client is connected to.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFiClientRead
Use client.stop() to disconnect from the server the client is
connected to.
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFIClientStop